Neurosurgeon for Spinal AVM Treatment in Dombivli
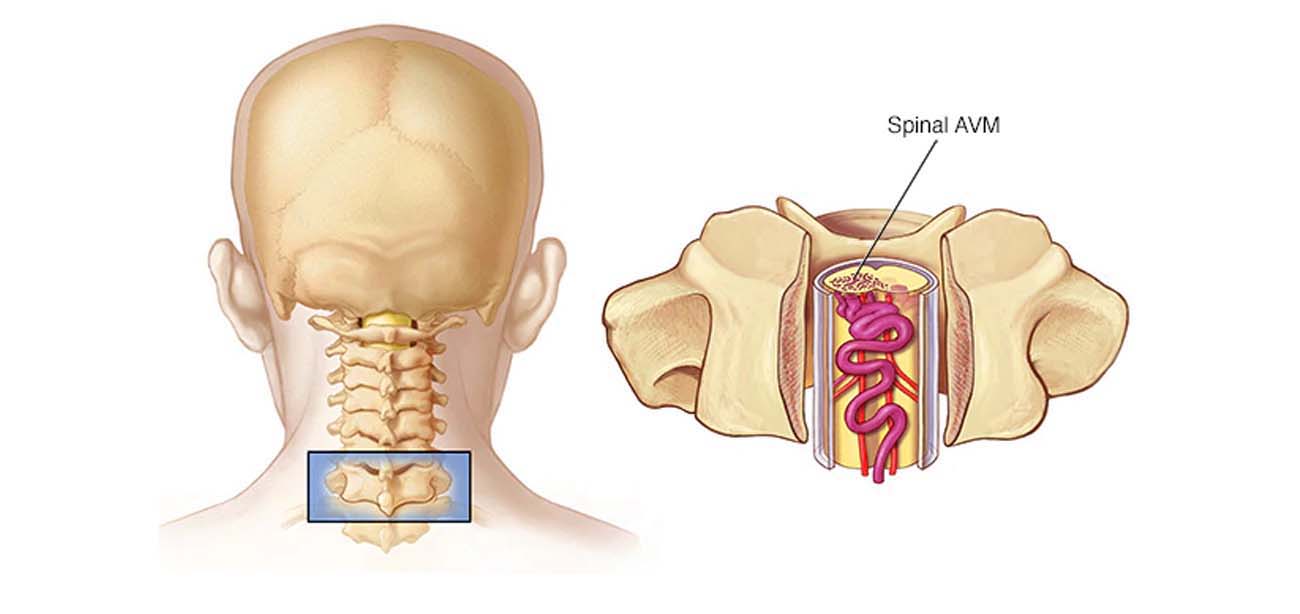
What is Spinal AVM ?
Spinal arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is a rare, abnormal tangle of blood vessels on, in or near the spinal cord. Without treatment, spinal AVM can permanently damage your spinal cord.
Diagnoses of Spinal AVM
Spinal arteriovenous malformations can be difficult to diagnose because signs and symptoms are similar to those of other spinal conditions, such as spinal dural arteriovenous fistula, spinal stenosis, multiple sclerosis or a spinal cord tumor.
Treatment
Treatment for spinal AVM may involve a combination of approaches to lessen symptoms as well as reduce the risk of potential complications. The choice of treatment will depend on the size, location and blood flow of your spinal AVM, your neurological exam, and your overall health.
The goal of spinal AVM treatment is to reduce the risk of hemorrhage and stop or prevent the progression of disability and other symptoms.
Treatment for Spinal Cord AVM includes:
Medication
Pain-relieving medications may be used to reduce symptoms such as back pain and stiffness, but most spinal AVMs will eventually require surgery.
Surgery
Surgery is usually needed to remove a spinal AVM from the surrounding tissue. There are three ways to remove the spinal AVM:
Procedures that are invovled are:
- Conventional Surgery. In this procedure, a surgeon makes an incision to remove the AVM, taking care to avoid damaging the spinal cord and other surrounding areas. Surgery is usually performed when the AVM is fairly small and in an area of the spinal cord that's easy to reach.
- Endovascular Embolization. Endovascular Embolization is a minimally invasive radiological procedure used to reduce the risk of hemorrhage and other complications associated with spinal AVMs.In endovascular embolization, a catheter is inserted into an artery in your leg and threaded to an artery in your spinal cord that is feeding your AVM. Small particles of a glue-like substance are injected to block the artery and reduce blood flow into the AVM. It doesn't permanently destroy the AVM. Your doctor may recommend endovascular embolization before conventional surgery to reduce the risk of bleeding during surgery or to reduce the size of the AVM so that surgery is more successful.
- Radiosurgery.This procedure uses radiation focused directly on the AVM to destroy the blood vessels of the malformation. Over time, those blood vessels break down and close up. Radiosurgery is most often used to treat small, unruptured AVMs.